SEP & FRAND before the UPC - what has been happening in 2024?
November 22 2024 was a landmark date in the Unified Patent Court (UPC) – it was the date the UPC issued its first decision involving a SEP and a FRAND defence.
The Mannheim Local Division (LD) granted Panasonic an injunction enforceable in five European countries, dismissing OPPO’s FRAND objection and counterclaim.
The LD’s decision was based on the fact that OPPO had not provided any of its own data relating to its own sales. The LD considered a willing licensee would provide this data so that the potential licensor would be fully informed. The LD therefore held that OPPO was not a willing licensee. The FRAND defence was therefore unsuccessful, and the LD did not go on to consider any specific terms for a FRAND license.
An injunction was granted in relation to Germany, France, Italy, the Netherlands and Sweden (the UPCA countries in which the patent is in force). OPPO was also ordered to recall/destroy products as well as provide information, accounting and damage compensation.
Background
Panasonic sued OPPO for infringement of six European Patents: three before the Mannheim LD (EP2568724, EP3096315, EP2207270) and three before the Munich LD (EP2197132, EP3024163 and EP2584854).
OPPO submitted a counterclaim for revocation and a counterclaim for a FRAND licence.
The Mannheim LD decided to hear all aspects of the case i.e. the infringement, the counterclaim for revocation and the counterclaim relating to a FRAND licence.
Proceedings continued under EP2568724, with the proceedings in relation to the other five patents apparently being swept into the proceedings under EP2568724.
The patent was considered valid & infringed
After some claim construction issues, the LD held EP2568724 to be valid (dismissing the counterclaim for revocation) and infringed by OPPO's 4G smartphones and smartwatches.
The Mannheim LD then considered OPPO's counterclaim relating to a FRAND defence.
The FRAND defence
This is the first decision issued by the UPC that has considered a FRAND defence.
The Mannheim LD referred mainly to the Huawei v. ZTE judgment by the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) - (Case C-170/13). This July 2015 judgment is the defining EU jurisprudence on the granting of an injunction when FRAND obligations are involved and has ever-since shaped court practice across the EU in relation to SEP cases.
Huawei v. ZTE, CJEU Case C-170/13, July 2015
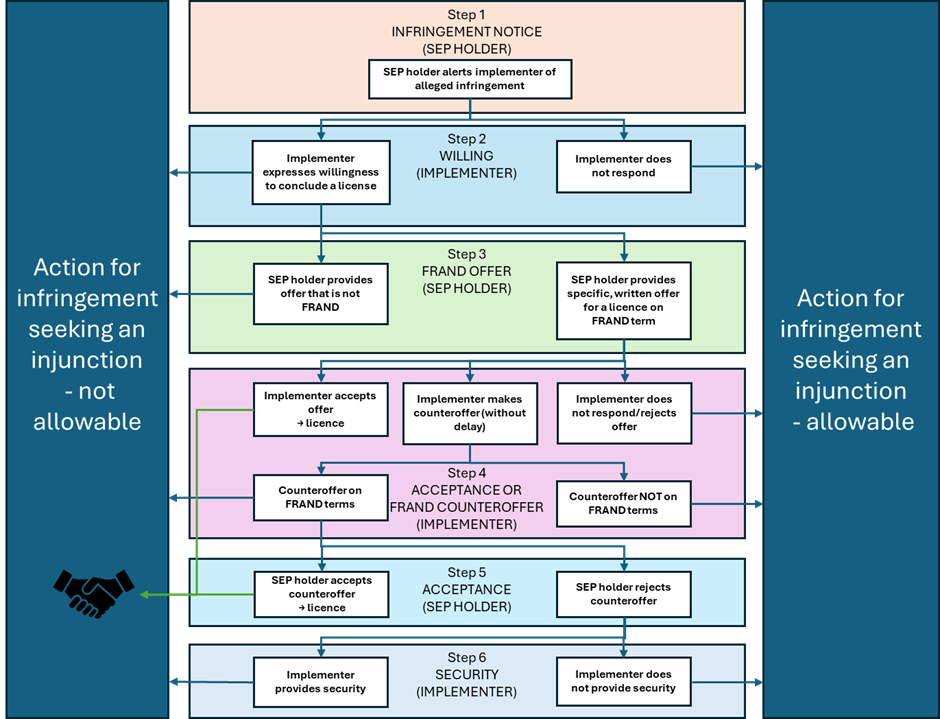
The outcome of Huawei v. ZTE is illustrated below.
According to Huawei v. ZTE, a SEP proprietor, which has given an irrevocable undertaking to grant a licence to third parties on FRAND terms, does not abuse its dominant position by bringing an action for infringement seeking an injunction as long as the following conditions are met:
- prior to bringing that action, the proprietor has:
- alerted the alleged infringer of the infringement complained about by designating that patent and specifying the way in which it has been infringed (Step 1), and,
- after the alleged infringer has expressed its willingness to conclude a licensing agreement on FRAND terms (Step 2), presented to that infringer a specific, written offer for a licence on such terms, specifying, in particular, the royalty and the way in which it is to be calculated (Step 3), and
- alerted the alleged infringer of the infringement complained about by designating that patent and specifying the way in which it has been infringed (Step 1), and,
- where the alleged infringer continues to use the patent in question,
- the alleged infringer has not diligently responded to that offer (step 4), in accordance with recognised commercial practices in the field and in good faith,
- this being a matter which must be established on the basis of objective factors and which implies, in particular, that there are no delaying tactics.
- the alleged infringer has not diligently responded to that offer (step 4), in accordance with recognised commercial practices in the field and in good faith,
A couple of subsequent steps (Steps 5 and 6) in relation to a counteroffer from the implementing alleged infringer were also defined, as illustrated below:
Since the CJEU judgment, national courts of the EU have repeatedly applied this framework of conditions. The questions the national courts have considered include:
- Does every SEP necessarily confer dominance to its holder?
- How detailed does an infringement notice need to be, particularly if a portfolio license is sought?
- When can the patent owner safely conclude that the user is an unwilling licensee and the seeking of an injunction is therefore justified?
- And, most importantly, how to determine a fair, reasonable, and non-discriminatory (‘FRAND’) license offer.
However, there has been some inconsistency across the EU states in regard to such questions. For instance, some national courts have decided that each step happens sequentially and that later actions cannot retroactively mean that an earlier step has been taken. Other national courts have decided that each step does not require sequentiality and that later actions can retroactively mean that an earlier step has been taken.
This has concerned the European Commission (EC) to such an extent that it recently took the rare step of filing an amicus curiae brief, in a patent infringement action pending at the Higher Regional Court Munich (6 U 3824/22 Kart HMD Global v. VoiceAge). The EC expressed its concern that the CJEU judgment was not being applied correctly and consistently across the EU.
The EC position's is that Step 1 requires specific details of the patent at issue and that it was not sufficient to just refer to, say, a website with general details of the SEP holder's SEPs. The EC also said that this has to happen before litigation starts and cannot be remedied later.
As far as Step 2 is concerned (which can be considered as ‘Willingness of Licensor’), the EC's position was that this needed to be explicit as well, and not conditional on things that might happen later.
The EC also indicated that all steps have to be taken before the injunction is sought, explaining that the purpose of the Huawei v. ZTE decision was to allow parties to negotiate without the fear of an injunction. The EC's view is that each step happens sequentially and that later actions cannot retroactively mean that an earlier step has been taken or not taken.
So what did the Mannheim LD decide?
The LD considered the willingness of the parties and ultimately dismissed OPPO’s defence on the facts of the case. The LD considered the offer from Panasonic to be FRAND but the counteroffer from OPPO not.
In considering OPPO’s counteroffer not to be FRAND, the decision relies on the fact that OPPO had not provided any of its own data relating to its own sales. The LD considered a willing licensee would provide this data, so that the potential licensor would be fully informed, and provide security on the resulting amount. The LD therefore held that OPPO was not a willing licensee.
The LD also considered the amicus curiae brief of the EC and concluded that each step does not require sequentiality and that…



